506 MEDICARE
Medicare is a government health insurance program for people 65 and over, some people under the age of 65 with disabilities, and people of any age living with permanent kidney failure. It pays for many health care expenses but does not cover them all.
Medicaid has limits on the type of care it will pay for and for how long. For example, Medicare covers only medically "reasonable and necessary" care and does not cover personal care that helps you with things like bathing, dressing, etc.
Generally, an individual is eligible for Medicare at age 65 or older if:
-
They are a U.S. citizen or a permanent legal resident who has lived in the United States for at least five years; and
-
They or their spouse has worked long enough to be eligible for Social Security or railroad retirement benefits - usually having earned 40 credits from about 10 years of work - even if they are not yet receiving these benefits; or
-
They or their spouse are a government employee or retiree who has not paid into Social Security but has paid Medicare payroll taxes while working.
An individual may qualify for Medicare under age 65 if:
-
They have been entitled to Social Security disability benefits SSDI (not including SSI) for at least 24 months (which need not be consecutive); or
-
They receive a disability pension from the Railroad Retirement Board and meet certain conditions; or
-
They have Lou Gehrig's disease (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis), which qualifies them immediately; or
-
They have permanent kidney failure requiring regular dialysis or a kidney transplant - and they or their spouse has paid Social Security taxes for a certain length of time, depending on their age.
If an individual age 65 or older does not qualify for Medicare based on their own or their spouses work record, they may still receive Medicare if:
-
They are a U.S. citizen or a legal resident for at least five years; and
-
They pay premiums for Part A, Part B, and Part D.
To be eligible for Medicaid, an individual who appears to be eligible for Medicare must apply for and enroll in Medicare coverage. See ADLTC MS 505 for information about Third Party Resources and ADLTC MS 510 for information about Assignment of Rights.
This includes individuals who receive Medicare Part A at no charge, but who have not elected Medicare Part B because they were not willing or able to pay the associated monthly premium.
If an individual is receiving Medicare Part A but not Part B, and they are eligible for a Medicare Savings Program as explained in ADLTC MS 580, email DHCS at DMATPL@alaska.gov requesting that they start the Medicare Savings Program. This will open Part B without having to pend the case.
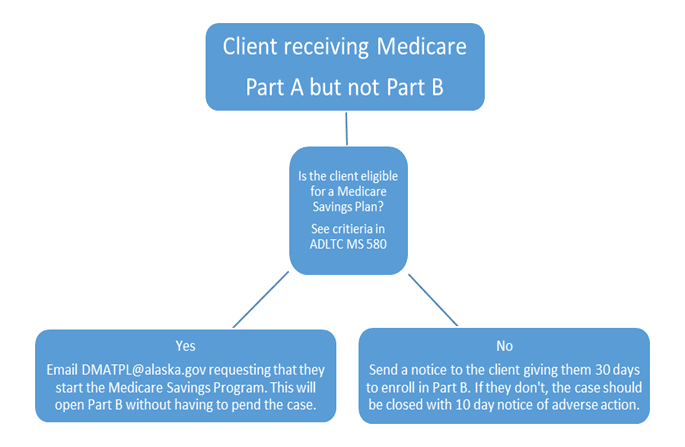
If the individual is not eligible for a Medicare Savings Program, refer them to the local Social Security Office to apply for Medicare. See ADLTC MS 506(J) for a listing of Social Security Office addresses and phone numbers.
The M008 - Medicare Benefits Available notice is used for this purpose. If the individual fails, without good cause to apply for the Medicare benefits within 30 days, the caseworker must deny the Medicaid application or close the Medicaid case.
Information from the SSA may be obtained by direct contact with the serving SSA office, or by viewing the SOLQ, SVES, or BENDEX interfaces.
Note:
The Medicaid application should not be delayed during the 30 day period allowed for application of Medicare. If the individual meets all other eligibility factors except for the application of Medicare, the Medicaid application should be approved.
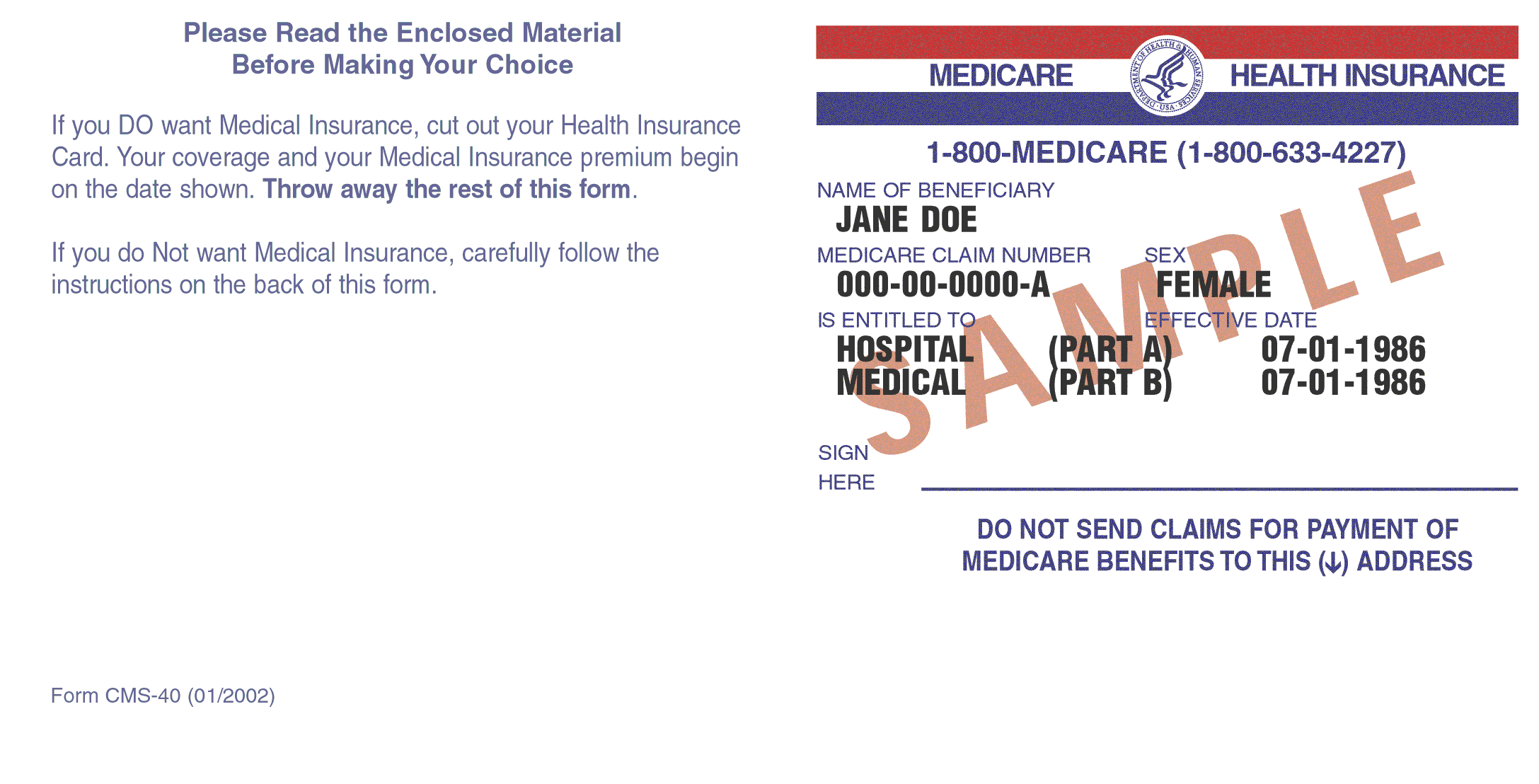
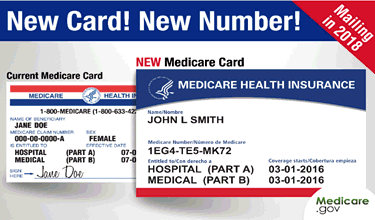
When Social Security determines that an individual is eligible for Medicare, the beneficiary will receive a red, white and blue Medicare Health Insurance card (as seen below). This card usually arrives about 3 months before the actual eligibility date.
The card will show the beneficiary's name, Medicare Beneficiary Identifier (MBI), sex, Part A and/or Part B effective dates, and the beneficiary's signature block. The Health Insurance Claim (HIC) number is being replaced by the MBI on the card. The HIC number will still be used by DHCS. To find the HIC number, use the SVES interface. The HIC number will still be entered in EIS and ARIES. DHCS will be collecting the MBI directly from CMS so there is no need to communicate the MBI to DHCS. If the client provides the MBI, it should be entered into the case note.
A recipient should present their Medicare card and the Medicaid Recipient Identification Card to health care providers as proof of both Medicare and Medicaid coverage. See Section 501(C) for policy using the Medicaid Recipient Identification Card or coupon. Subsequent Medicare cards issued, in addition to Bendex updates, will reflect the newest effective dates. A photocopy of the recipients Medicare Card should be kept in the case file.
506 D. MEDICARE PART A THROUGH D
1. Part A - Hospital Insurance
Part A helps cover:
-
Inpatient care in a hospital
-
Inpatient care in a skilled nursing facility (not custodial or long term care)
-
Hospice care
-
Home health care
-
Inpatient care in a religious nonmedical health care institution
Most people who have Part A do not pay monthly premiums because they have at least 10 years of Medicare covered employment. Those who do not have 10 years of employment must pay a monthly premium. See Addendum 1.
Individuals who begin receiving Social Security benefits at age 65 are enrolled in free Medicare Part A at the same time.
Disabled individuals who receive Social Security Disability Insurance ( SSDI ) are automatically enrolled in Medicare Part A after 24 months. Disabled individuals receiving SSI benefits do not automatically qualify for Medicare Part A. Once they reach age 65, they may be eligible for Medicare Part A, but they are charged a premium.
2. Part B - Supplementary Medical Insurance
Part B helps cover:
-
Services from doctors and other health providers
-
Outpatient care
-
Home health care
-
Durable medical equipment (like wheelchairs, walkers, hospital beds, and other equipment and supplies)
-
Many preventative services (like screenings, shots, and yearly "wellness" visits)
3. Part C - Medicare Advantage Plans
While the majority of people with Medicare get their health coverage from Original Medicare, some choose to get their benefits from a Medicare Advantage Plan, also known as a Medicare private health plan or Part C. Medicare Advantage Plans contract with the federal government and are paid a fixed amount per person to provide Medicare benefits.
Many Medicare Advantage Plans also offer prescription drug coverage (Part D).
4. Part D - Prescription Drug Coverage
Part D helps cover:
-
Costs of prescription drugs
Part D plans are run by private insurance companies that follow rules set by Medicare.
To be eligible for Medicare Part D prescription drug coverage, the beneficiary must be entitled to Part A or enrolled under Part B. The beneficiary does not need both Part A and Part B coverage to choose prescription drug coverage.
Medicare Part D prescription drug coverage replaces Medicaid prescription drug coverage for recipients who are eligible for both programs. Medicare pays for prescription drugs through private plans.
People with both Medicare and Medicaid, known as "dual eligible", are automatically enrolled in a plan. An applicant or recipient who has other creditable prescription drug coverage, such as employer or union coverage (including COBRACOBRA ) is not required to join a Medicare drug plan. This is because an applicant or recipient who drops employer or union coverage may not be able to get it back. This may also affect coverage for spouses and dependents. Applicants and recipients should be instructed to call Medicare at 1-800-633-4227 or the plan listed in their letter telling them they don't want to be in a Medicare drug plan. TTY users can call 1-877-486-2048.
Persons who have been automatically assigned to a prescription drug plan can opt-out of a plan, or change plans at any time as long as they remain eligible for Medicaid. However, if a person chooses to opt-out of a prescription drug plan without enrolling in another plan, Medicaid will not pay for the cost of their prescription drugs, and he or she will have a lapse in drug coverage.
Note:
Send EIS notice "M710 - Medicare Drug Coverage Begins" when a Medicaid applicant has Medicare, and when a recipient becomes eligible for Medicare.
506 E. HEALTH INSURANCE CLAIM NUMBER
The Medicare card shows the type of health insurance the person has, the effective date of the coverage, and the health insurance claim ( HIC ) number. This may be his/her own SSN , a spouse or parent SSN, and will have a suffix further clarifying eligibility type.
Note:
The HIC # may be changed by SSA with subsequent changes in eligibility. If this occurs, update the MERE screen accordingly and send an email to DMATPL@alaska.gov so the Medicare Savings Program can be corrected.
506 F. DISABILITY CLAIM NUMBER SUFFIX HA
When Medicare eligibility is based upon an individual’s disability, the SSA adds a suffix of HA to the beneficiary's SSN to indicate a disability claim. This number is not to be confused with a Health Insurance Claim number ( HIC #). The disability claim number, which will look like 123456789HA, will appear on all SSA correspondence to the beneficiary regarding his/her disability claim, including Medicare coverage related to that disability. This number should not be entered to MERE as the HIC # as it will interfere with Medicare Savings Program. Enter the accurate HIC # from the Medicare Card or BENDEX update. If these are not available, this information may be obtained from the SSA or DHCS.
Railroad beneficiaries have claim numbers consisting of 6 or 9 digits that do not fit into the HIC # field on MERE without conversion. The caseworker should first document the Railroad Claim Number exactly as it appears on the RRB Medicare card in a case note ( CANO ) and then notify DHCS who will make a conversion to the appropriate ID number for input to EIS . Verification of Railroad benefits may be made by contacting the Railroad Retirement Board toll free at 1-800-808-0772.
506 H. MEDICARE SAVINGS PROGRAMS
Medicaid recipients who are Medicare eligible are automatically eligible for and enrolled in the Low-Income Subsidy (LIS) Program. Depending on countable income and resources, they may also be eligible for a Medicare Savings Program. Please see ADLTC MS 580 for additional information.
The SSA produces the State Data Exchange ( SDX ), the Beneficiary Data Exchange (BENDEX), and the State Verification Exchange System (SVES) information systems. Information from these sources is useful in determining who is eligible for or receiving Part A or Part B.
SDX contains a record of all people who are eligible for SSI payments or federally administered state supplements.
BENDEX provides only the data exchange that the state has requested. The BENDEX file provides SSA payment status, SSI payment status and Medicare eligibility, Supplemental Medical Insurance premium (Part B) payer, changes to HIC #, and Medicare entitlement dates. SSA sends Bendex data to the state each time a change occurs to the beneficiary record or household.
SVES provides data when an inquiry is initiated on EIS. A response is returned to EIS within approximately three working days. The information from the SVES response from SSA verifies social security number, social security, Title II benefits, and supplemental security income.
506 J. SOCIAL SECURITY OFFICES
The following Social Security offices and telephone/fax numbers are available to the public:
|
SSA National Number: |
1-800-772-1213 |
|
TTY Users: |
1-800-325-0778
|
| Anchorage
222 W. 8th Ave, RM A11 Anchorage, AK 99513 907-271-4455 1-866-772-3081 907-271-4878 (fax) 907-271-6807 (back-up fax)
|
Juneau
709 W. 9th Street, RM 231 PO Box 21327 Juneau, AK 99802 1-800-478-7124 907-586-7620 (fax)
|
| Fairbanks
101 12th St., RM 138 Fairbanks, AK 99707 907-456-5390 1-800-478-0391 907-456-0333 (fax) |
Ketchikan
628 Mill St., RM 503 Ketchikan, AK 99901 907-225-5200 1-800-478-5199 907-225-8976 (fax) |
|
|
||
|
|
|